Introduction
The exponential growth of technology has created an invisible crisis – electronic waste is now the fastest-growing waste stream worldwide. While consumers enjoy constant device upgrades, discarded smartphones, laptops, and gadgets are poisoning our planet at an alarming rate. This investigative report exposes the shocking truth about e-waste, its global impact, and actionable solutions for a more sustainable digital future.
A. The Global E-Waste Crisis
1. Staggering Statistics
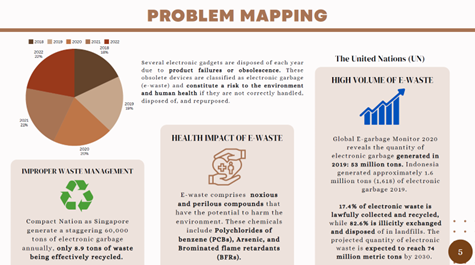
- 62 million tons generated annually (equivalent to 6,200 Eiffel Towers)
- Only 17.4% properly recycled (UN Global E-Waste Monitor)
- Growing 3x faster than other waste streams
- $65 billion in lost value from unrecovered materials
2. Toxic Components
| Material | Health Risks | Environmental Damage |
|---|---|---|
| Lead | Brain damage | Soil contamination |
| Mercury | Nervous system harm | Water pollution |
| Cadmium | Kidney failure | Bioaccumulation |
| Flame retardants | Cancer risk | Air pollution |
3. Global Disposal Patterns
- 75% shipped illegally to developing nations
- Major dumping grounds: Ghana, India, China
- Informal recycling exposes workers to deadly toxins
B. Drivers of the E-Waste Epidemic
1. Planned Obsolescence
- Manufacturers limit device lifespans
- Irreplaceable batteries in modern devices
- Software updates that slow older models
2. Consumer Behavior
- Average smartphone lifespan: 2.5 years
- 50% of discarded electronics still functional
- “Upgrade culture” fueled by marketing
3. Recycling Challenges
- Complex device disassembly requirements
- Hazardous material handling costs
- Lack of global standards
C. Health and Environmental Impacts
1. Human Toll
- 18 million informal e-waste workers worldwide
- Children’s IQ reduced by 5 points in dumping zones
- Cancer rates 45% higher near e-waste sites
2. Ecological Damage
- 23% of global mercury pollution from e-waste
- 1 computer monitor contaminates 80,000 liters of water
- Microplastics from electronics entering food chain
3. Climate Connection
- Mining new materials creates 3x more emissions than recycling
- Data centers discard 2 million servers annually
- E-waste accounts for 0.3% of global CO2 emissions
D. Solutions and Innovations
1. Corporate Responsibility
- Apple’s robot disassembles 200 iPhones/hour
- Fairphone’s modular design philosophy
- Dell’s closed-loop recycling program
2. Policy Interventions
- EU Right to Repair legislation
- Extended Producer Responsibility laws
- Basel Convention amendments
3. Consumer Action Guide
A. Extend device lifespan with proper care
B. Choose repairable, upgradable products
C. Use certified e-waste recyclers
D. Support sustainable electronics brands
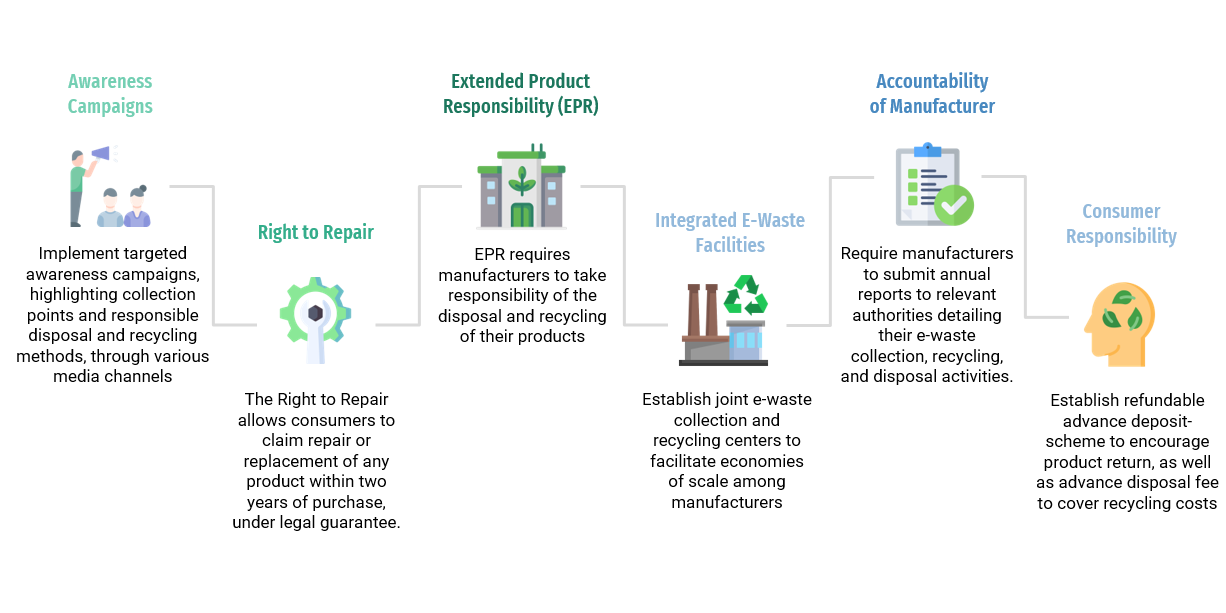 E. The Circular Economy Future
E. The Circular Economy Future
1. Emerging Technologies
- AI-assisted sorting systems
- Bioleaching for metal recovery
- Modular device architectures
2. Economic Opportunities
- Urban mining could recover $14 billion in gold annually
- Recycling creates 15x more jobs than landfills
- Secondhand tech market growing 20% yearly
3. What You Can Do Today
- Calculate your e-footprint
- Organize community recycling drives
- Advocate for stronger regulations
Conclusion
The e-waste crisis represents the dark underbelly of our digital revolution. While technology advances at lightning speed, we must develop equally innovative solutions to manage its afterlife. Through conscious consumption, corporate accountability, and policy reform, we can work toward a future where technological progress doesn’t come at the planet’s expense.
Tags: e-waste, electronic waste, digital pollution, sustainable technology, right to repair, recycling, toxic waste, environmental impact, circular economy, responsible consumption
Category: Environment & Technology