The rollout of 5G technology marks a transformative leap in global connectivity, promising unprecedented speeds, ultra-low latency, and massive device connectivity. As the fifth generation of wireless technology, 5G is set to redefine industries, enable smart cities, and power the Internet of Things (IoT) on an unprecedented scale. This comprehensive guide explores 5G’s technological advancements, real-world applications, challenges, and future potential.
A. Understanding 5G Technology
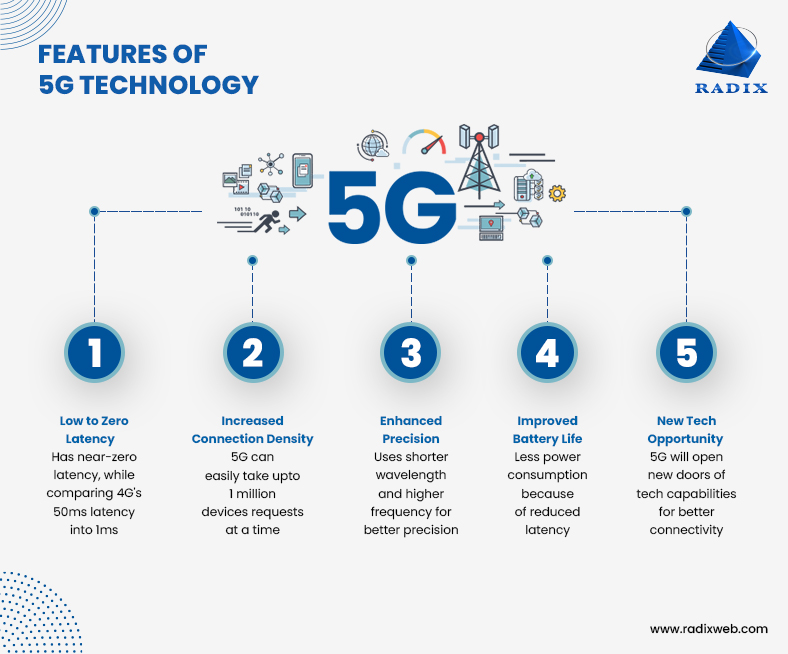
1. What Makes 5G Different?
5G represents a quantum leap over previous generations with three key improvements:
- Enhanced Speed: Up to 100x faster than 4G (potential speeds of 10 Gbps)
- Ultra-Low Latency: As low as 1ms delay, critical for real-time applications
- Massive Connectivity: Supports up to 1 million devices per square kilometer
2. Core Technologies Powering 5G
- Millimeter Waves (mmWave): High-frequency bands (24-100 GHz) enabling blazing speeds
- Small Cell Networks: Dense clusters of miniature base stations for urban coverage
- Network Slicing: Creating multiple virtual networks on shared infrastructure
- Beamforming: Directing signals to specific users rather than broadcasting
3. The Evolution from 1G to 5G
- 1G (1980s): Analog voice calls
- 2G (1990s): Digital calls and SMS
- 3G (2000s): Mobile internet access
- 4G (2010s): Streaming and app economy
- 5G (2020s): IoT, AR/VR, and mission-critical communications
B. Transformative Applications of 5G
1. Smart Cities and Infrastructure
- Traffic Management: Real-time monitoring reduces congestion by 30%
- Public Safety: AI-powered surveillance with instant emergency response
- Utility Management: Smart grids adjusting energy distribution dynamically
2. Healthcare Revolution
- Remote Surgery: Surgeons operate via robotic arms with near-zero latency
- Wearable Tech: Continuous health monitoring with instant doctor alerts
- AR-Assisted Diagnostics: Doctors visualize scans in 3D during examinations
3. Industrial Automation (Industry 4.0)
- Predictive Maintenance: Sensors detect equipment failures before they occur
- Autonomous Robots: Real-time coordination in manufacturing plants
- Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of factories for optimization
4. Entertainment and Media
- Cloud Gaming: Console-quality games streamed to mobile devices
- 8K Live Streaming: Ultra-high-definition broadcasts without buffering
- Immersive AR/VR: Fully interactive virtual experiences
5. Autonomous Vehicles
- V2X Communication: Cars “talk” to traffic lights and other vehicles
- Fleet Management: Real-time routing for delivery trucks
- Safety Systems: Instant collision avoidance responses
C. Global Implementation and Challenges
1. Current Deployment Status
- Leading Countries: South Korea (95% coverage), China (1.5M+ base stations), USA (major cities)
- Emerging Markets: India and Africa rolling out 5G in urban centers
2. Technical Challenges
- Infrastructure Costs: $1 trillion estimated global investment needed
- Signal Obstruction: Millimeter waves struggle with buildings and trees
- Energy Consumption: Base stations require 3x more power than 4G
3. Security and Privacy Concerns
- Cyberattack Vulnerability: More entry points for hackers
- Data Privacy: Location tracking becomes more precise
- Geopolitical Tensions: Huawei ban in multiple Western countries
4. Health and Environmental Debates
- Radiation Fears: Ongoing studies about long-term effects
- E-Waste: Accelerated device replacement cycles
- Energy Efficiency: Balancing performance with sustainability
D. The Future of 5G: What’s Next?
1. 5G-Advanced (2025-2030)
- AI Integration: Self-optimizing networks
- Extended Reality (XR): Blending physical and digital worlds
- Tactile Internet: Haptic feedback over networks
2. 6G Horizon (2030+)
- Terahertz Frequencies: Potential 1TBps speeds
- AI-Native Networks: Fully autonomous systems
- Space-Terrestrial Integration: Satellite and ground networks merging
3. Economic Impact Projections
- $13.2 Trillion in global economic value by 2035
- 22 Million Jobs created worldwide
- 35% Productivity Boost in key industries
E. Preparing for the 5G Era
1. For Consumers
- Upgrade to 5G-compatible devices
- Explore cloud-based services and IoT devices
- Understand data privacy settings
2. For Businesses
- Invest in 5G-enabled IoT solutions
- Train staff on 5G applications
- Partner with telecom providers for custom solutions
3. For Governments
- Accelerate infrastructure development
- Establish cybersecurity frameworks
- Fund 5G research and startups
Conclusion
5G technology is more than just faster smartphones—it’s the foundation for a fully connected digital ecosystem that will transform how we live, work, and interact. While challenges remain in implementation and security, the potential benefits across healthcare, industry, and urban development make 5G one of the most significant technological advancements of our era.
Tags: 5G technology, wireless innovation, IoT connectivity, smart cities, 5G applications, network infrastructure, mobile technology, future of communication, 5G security, digital transformation