Introduction
Digital advertising has evolved into a sophisticated ecosystem that tracks, analyzes, and influences consumer behavior with frightening precision. Behind every ad you see lies a complex web of data collection, machine learning algorithms, and psychological manipulation. This eye-opening guide reveals the hidden mechanisms of digital ad targeting, the data sources used, and how to protect your privacy in an increasingly monitored online world.
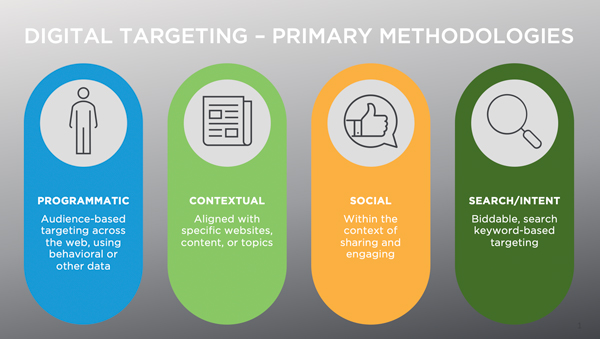
A. The Digital Advertising Ecosystem
1. Key Players in Ad Targeting
- Ad Networks (Google Ads, Facebook Audience Network)
- Data Brokers (Acxiom, Experian) collecting & selling personal data
- Demand-Side Platforms (DSPs) automating real-time ad buying
- Publishers hosting targeted ads on websites/apps
2. Market Size & Growth
- Global digital ad spend: $680 billion in 2024
- Programmatic advertising accounts for 88% of all digital ads
- The average person sees 6,000-10,000 ads daily
B. Data Collection Methods
1. First-Party Tracking
- Website cookies (session & persistent)
- Login credentials & account profiles
- Purchase histories & customer databases
2. Third-Party Surveillance
- Cross-site tracking pixels
- Device fingerprinting (browser/OS/hardware IDs)
- Mobile ad IDs (IDFA on iOS, AAID on Android)
3. Offline Data Merging
- Credit card purchase records
- Loyalty program activity
- Public records (voter registration, property deeds)
4. Behavioral Tracking Matrix
| Data Type | Collection Method | Advertising Use |
|---|---|---|
| Browsing History | Cookies, ISP logs | Interest-based targeting |
| Location Data | GPS, WiFi triangulation | Geo-targeted promotions |
| Social Activity | Likes, shares, follows | Psychographic profiling |
| Device Usage | App sensors, usage patterns | Cross-device targeting |
C. Targeting Technologies & Techniques
1. Demographic Targeting
- Age, gender, income level
- Education, marital status
- Homeownership, parental status
2. Behavioral Targeting
- Purchase intent modeling
- Content consumption patterns
- Micro-moment tracking
3. Psychographic Profiling
- Personality trait analysis
- Emotional state detection
- Political/religious leanings
4. Advanced Methods
- Lookalike Audiences (finding clones of existing customers)
- Predictive Analytics (forecasting future purchases)
- Programmatic Native Ads (disguised as organic content)
D. Real-World Targeting Examples
1. Facebook’s Shadow Profiles
- Tracks non-users across the web
- Builds profiles from friends’ contact lists
- Estimates interests from associated devices
2. Google’s Search Leakage
- Ties search history to YouTube viewing
- Connects Gmail content to ad preferences
- Links Android usage to Chrome browsing
3. Retail Surveillance
- Walmart tracks in-store movements via WiFi
- Target predicts pregnancies before announcements
- Amazon’s dynamic pricing based on user profiles
E. Psychological Manipulation Tactics
1. Neuromarketing Principles
- Color psychology in ad design
- Scarcity & urgency triggers
- Social proof engineering
2. Addiction Patterns
- Variable reward schedules
- Infinite scroll architectures
- Notification dopamine hits
3. Emotional Exploitation
- Mood-targeted advertising
- Trauma-based marketing
- Fear & anxiety stimulation
F. Protecting Yourself from Targeting
1. Technical Defenses
- Ad blockers (uBlock Origin, AdGuard)
- Privacy browsers (Brave, Firefox Focus)
- VPN services to mask IP addresses
2. Account Settings
- Opt-out of ad personalization
- Disable ad tracking on mobile devices
- Clear cookies regularly
3. Behavioral Changes
- Use separate browsers for different activities
- Avoid social media logins on other sites
- Regularly audit app permissions
 G. The Future of Ad Targeting
G. The Future of Ad Targeting
1. Emerging Technologies
- AI-generated hyper-personalized ads
- Emotion recognition through webcams
- AR advertising in physical spaces
2. Regulatory Challenges
- GDPR & CCPA compliance hurdles
- The cookieless future (Google’s FLoC alternative)
- Global pushback against surveillance capitalism
3. Ethical Considerations
- Mental health impacts of micro-targeting
- Democracy & manipulation risks
- The right to digital anonymity
Conclusion
The advertising industry has built an invisible surveillance machine that knows you better than you know yourself. While targeted ads power “free” online services, the psychological and privacy costs remain largely hidden. As tracking technologies grow more sophisticated, consumers must educate themselves and demand greater transparency from the tech giants profiting from their attention.
Tags: digital advertising, ad targeting, online privacy, data tracking, behavioral advertising, surveillance capitalism, ad tech, marketing technology, consumer privacy, targeted ads
Category: Digital Marketing & Privacy